REFER investigated the impact of the FreeStyle Libre system on HbA1c in type 2 diabetes (T2D) managed with basal-bolus insulin treatment.1
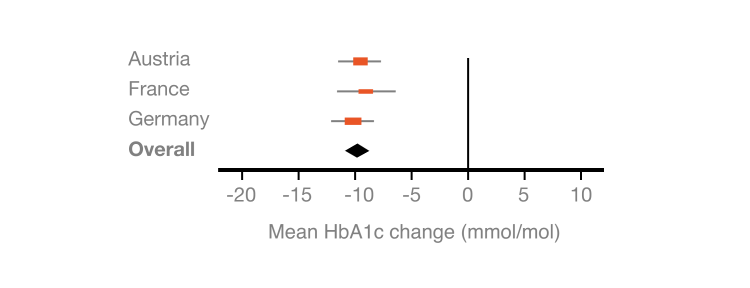
Real-world data were collected in 3 parallel, retrospective, non-interventional chart review studies of type 2 diabetes patients using the FreeStyle Libre system at diabetes centres in Austria, France and Germany.
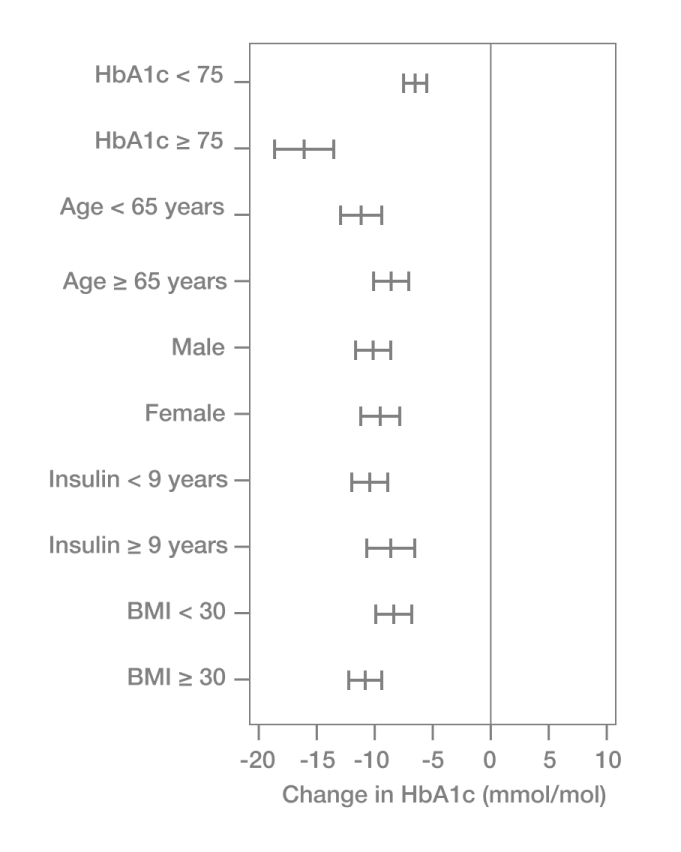
In these real-world settings, using the FreeStyle Libre system for 3–6 months significantly reduced HbA1c levels in people with T2D managed with basal-bolus insulin therapy.
.svg)