Uncompromising Quality
FreeStyle Libre 2 and Libre 3 systems meet iCGM1 standards for accuracy studies.



Uncompromising quality
State-of-the-art manufacturing
with sensor quality ensured through rigorous testing and precise factory-calibration.
Smart quality checks
so your patients can rely on every reading they get. Every sensor conducts over 20,000 self-checks during its wear period.
Proven performance
with documented highest levels of safety and accuracy,2 supported by peer-reviewed clinical studies demonstrating real-world results3-5 and routine post-market quality monitoring.
Trusted data security
to ensure adherence to local privacy and cybersecurity standards, and to strive to safeguard all personal health data.
Commitment to customer care
with a specialist team available to help with simple or complex questions, as well as quick and free of charge sensor replacements for patients.
iCGM accuracy criteria
CE certification has performance standards for other medical devices6
The CE mark is well established for certifying process quality but does not have defined CGM accuracy and performance standards.6
- CGM-specific performance standards are needed for a rigorous approval process6
- European KOLs suggest adopting iCGM from the U.S. as an interim solution for acceptable CGM performance standards6
- CE certification combined with CGM-specific standards will result in better accuracy and safety for those with diabetes6
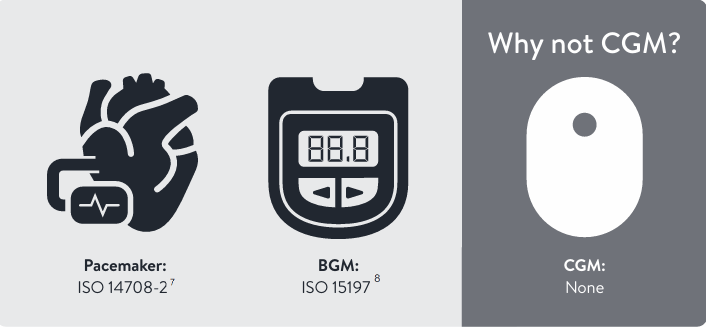 In the absence of minimum CGM performance standards in CE certification, look for a CGM device with CE certification and iCGM designation
In the absence of minimum CGM performance standards in CE certification, look for a CGM device with CE certification and iCGM designation
iCGM designation is not just a standard, it's patient safety
Not all CGMs are created equal9
Patient safety concerns are being raised due to poor accuracy at low and high glucose levels of CGMs not meeting rigorous accuracy standards9
Additional safeguards to CE Mark are needed10
Rigorous accuracy and performance standards are needed urgently6
MARD alone is
not enough
not enough
MARD may not reflect clinical accuracy across the entire glucose range11
Rigorous standards enhances accuracy
US-FDA iCGM standards are the most rigorous of any major regulatory body to ensure patient safety1.9
Meet iCGM standards for accuracy studies1
- Backed by robust clinical data
Includes peer-reviewed studies or data available on regulatory body platforms12,13
- Representative of performance across the target population and sensor wear period12,13
Accurate across Type 1, Type 2, adults, and children throughout sensor wear12,13
- Proven performance across the dynamic glycaemic range12,13
Especially in the hypoglycaemic range, where clinical accuracy is most critical
Note: When choosing a CGM, please ask if the device meets rigorous accuracy standards such as iCGM.
Clinical insights
Understanding CGM Comparison Charts
Get an insight into how to interpret CGM evaluation tools for confident prescribing
This quick, evidence-based guide developed by UK experts helps HCPs compare CGM systems for insulin dosing, outlining accuracy, regulation, and study design.
Use this guide to:
- Assess how CGMs systems have been tested for insulin dosing
- Understand key clinical and regulatory benchmarks
- Give you confidence when selecting a CGM system
Source: Diabetes Specialist Nurse Forum UK. This link is provided with the consent of the chart's owner and is intended for informational purposes only.

Evidence-based perspectives on CGM safety
Get an insight how to evaluate CGM systems using clinical and real-world data
Explore a CME module led by global experts to understand why CGM accuracy matters and how to evaluate iCGM vs. non-iCGM systems using current evidence.
The module includes:
- Why CGM accuracy matters in everyday practice
- What the data says about integrated CGM (iCGM) systems
- How iCGM and non-iCGM devices differ in clinical use

Key Articles on CGM Accuracy and Standards
Minimum expectations for market authorization of continuous glucose monitoring devices in Europe
- Chantal Mathieu, 2024
Importance of FDA-Integrated Continuous Glucose Monitors to Ensure Accuracy of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- David C. Klonoff, 2024
References & Disclaimers
Images are for illustrative purposes only. Not real patient or data.
1. iCGM is a US FDA regulatory designation that is only applicable in the US. https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-H/part-862/subpart-B/section-862.1355
2. Data on file, Abbott Diabetes Care, Inc.
3. Evans M, Welsh Z, Ells S, Seibold A. The Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring on Glycaemic Control as Measured by HbA1c: A Meta-analysis of Clinical Trials and Real-World Observational Studies. doi:10.1007/s13300-019-00720-0.
4. Carlson AL, Daniel TD, DeSantis A, et al. Flash glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes managed with basal insulin in the USA: a retrospective real-world chart review study and meta-analysis. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002590.
5. Riveline JP, Roussel R, Vicaut E, de Pouvourville G, Detournay B, Emery C, Levrat-Guillen F, Guerci B. Reduced Rate of Acute Diabetes Events with Flash Glucose Monitoring Is Sustained for 2 Years After Initiation: Extended Outcomes from the RELIEF Study. doi:10.1089/dia.2022.0085.
6. Mathieu, C. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism (2024): https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.16153.
7. Requirements for active implantable medical devices intended to treat bradyarrhythmais (pacemakers) to provide basic assurance of safety.
8. Performance requirements for in vitro glucose monitoring systems that measure glucose concentrations in capillary blood samples.
9. Klonoff, D. C.Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology (2024). https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/19322968241250357.
10. Alva et al. Diabetes SciTechnol (2025).https://doi.org/10.1177/19322968251329364.
11. Heinemann, L. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology (2020). https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1932296819855670
12. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K193371.pdf. Accessed June 2025.
13. Alva S, Bailey T, Brazg R, et al. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology (2020): 16(1):70-77. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296820958754.
The sensor housing, FreeStyle, Libre, and related Grand marks are marks of Abbott. Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
ADC-115230 v1.0
.svg)


