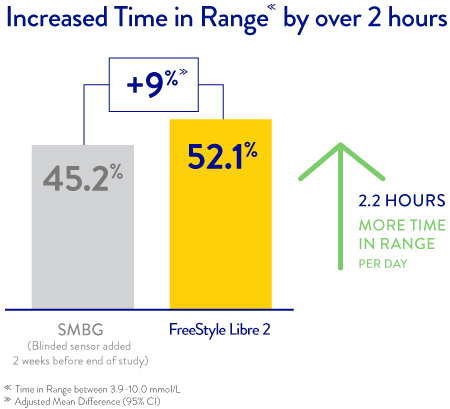
An independent study published in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that FreeStyle Libre 2 users increased their Time in Range by over 2 hours per day.
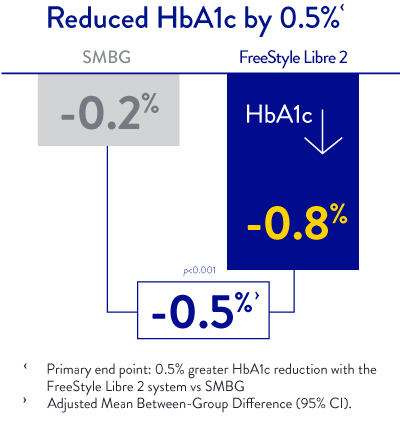
The same independent study shows that FreeStyle Libre users reduced their HbA1c by 0.5% compared to self-monitored blood glucose at 6 months of use.
vs -0.33% with BGM (p=0.005)
RCT of n=101 people with T2DM on MDI therapy
p<0.0001 vs baseline
Meta-analysis of data from 18 medical centres in Austria, France and Germany
n=363
(<3.9 mmol/L)
(p=0.0006)
Real World data showed that 95% of patients with T1D and T2D using the FreeStyle Libre system have a better understanding of their glucose fluctuations.5
Patients with T2D who make lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, see improved glucose control.6

increase in time in range
(3.9–10.0 mmol/L)
reduction in HbA1c7
less time spent in hyperglycaemia7
(>10 mmol/L) with no significant increase in time spent in hypoglycaemia (<3.9 mmol/L)
of children and teenagers agreed that the FreeStyle Libre system did not get in the way of daily activities7
Analysing the impact of the FreeStyle Libre portfolio on the lives of real users.
Learn more about Time in Range and the FreeStyle Libre portfolio through our Healthcare Professional educational modules.
We offer various on-demand webinars for Healthcare Professionals including a spotlight on hypoglycaemia.
Learn more about Time in Range in our CME accredited three-module webcast series.
Explore our training resources to help you to help your patients understand Time in Range better.
References & Disclaimers
Images are for illustrative purposes only. Not real patient or data.
* FreeStyle Libre systems refers to the FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 systems. The data from this study was collected using the FreeStyle Libre 2 system. FreeStyle Libre 3 system has the same features as the FreeStyle Libre 2 system therefore the study data is applicable to both products.
Ѱ For children aged 4-12, a caregiver at least 18 years old is responsible for supervising, managing, and assisting them in using the FreeStyle Libre system and interpreting its readings.
1. Leelarathna, L. N Engl J Med. (2022): DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2205650.
2. Yaron M, et al. Effect of flash glucose monitoring technology on glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019;42(7):1178–84.
3. Kröger J, et al. Three European retrospective real-world chart review studies to determine the effectiveness of flash glucose monitoring on HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther 2020;11(1):279–91.
4. Haak T, et al. Flash glucose-sensing technology as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring for the management of insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Ther 2017;8(1):55–73.
5. Fokkert M, van Dijk P, Edens M, et al. Improved well-being and decreased disease burden after 1-year use of flash glucose monitoring (FLARE-NL4). BMJ Open Diab Res Care. 2019. https://doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000809.
6. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 5. Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45 (Suppl. 1):S60–S82.
7. Campbell FM, et al. Outcomes of using flash glucose monitoring technology by children and young people with type 1 diabetes in a single arm study. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19(7):1294–301.
The "Yes" link below will take you to a website other than Abbott Laboratories. Links to other websites are not under the control of Abbott Laboratories, and Abbott Laboratories is not responsible for the content of such websites or any link contained in such websites. Abbott Laboratories is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Abbott Laboratories of the site.
Do you want to leave this page?
If you're a healthcare professional located in a different country, please select your country's website from the list of our global sites or contact your local Abbott representative for correct information about the products available in your country.
If you're not a healthcare profressional, click here to go to the FreeStyle Libre consumer website for the UK.
Stay connected